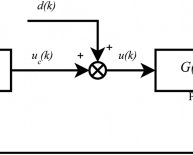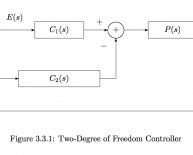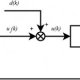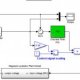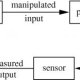
Closed loop electrical circuit
The voltage changes around any closed loop must sum to zero. No matter what path you take through an electric circuit, if you return to your starting point you must measure the same voltage, constraining the net change around the loop to be zero. Since voltage is electric potential energy per unit charge, the voltage law can be seen to be a consequence of conservation of energy.
The voltage law has great practical utility in the analysis of electric circuits. It is used in conjunction with the in many circuit analysis tasks.
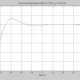
The voltage law is one of the main tools for the analysis of electric circuits, along with, the and the power relationship. Applying the voltage law to the above circuits along with Ohm's law and the rules for combining resistors gives the numbers shown below. The determining of the voltages and currents associated with a particular circuit along with the power allows you to completely describe the electrical state of a direct current circuit.